it’s crucial to explore and understand various dietary components and supplements that offer distinct advantages. One such comparison that has gained attention is the use of ethyl esters versus linseed oil, particularly in the context of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation. Examining the benefits of ethyl esters sheds light on why they are favored by some individuals seeking to enhance their health and well-being.
Understanding Ethyl Esters
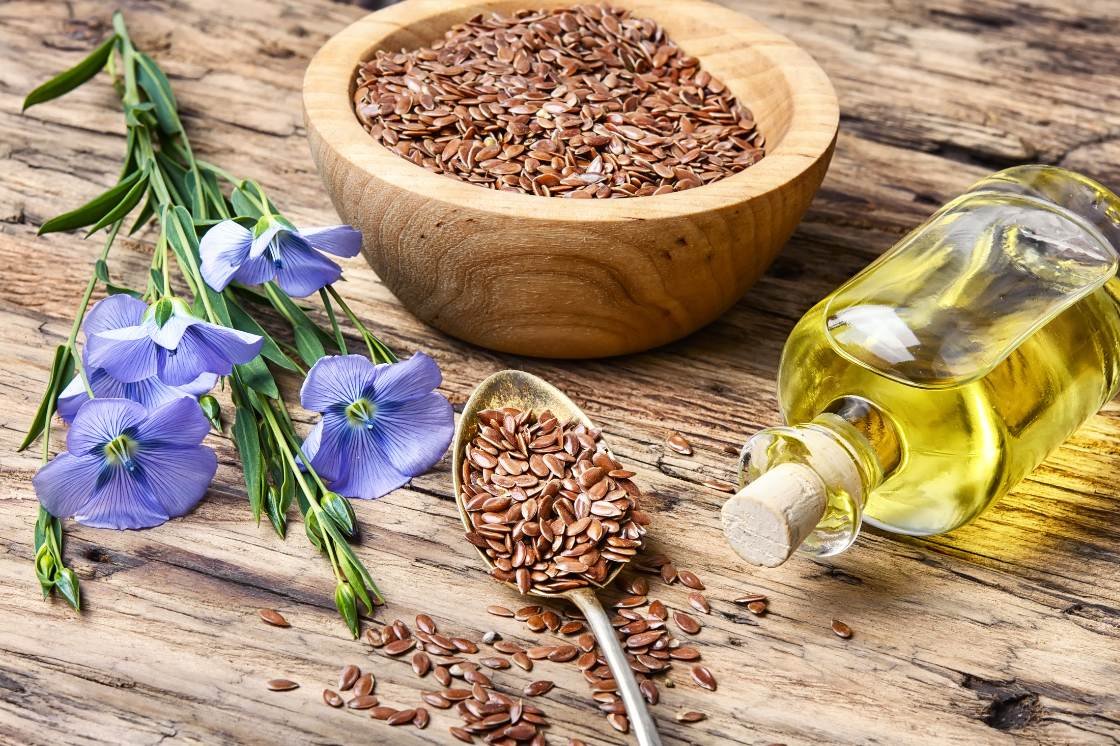
Ethyl esters are a molecular form of omega-3 fatty acids, primarily eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), often found in fish oil supplements. They are created by modifying the molecular structure of the fatty acids, making them more stable and bioavailable for human consumption. In contrast, linseed oil, derived from flaxseeds, is a source of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), another type of omega-3 fatty acid.
Few of the Advantages of Ethyl Esters:
Higher Concentration of EPA and DHA: Ethyl ester supplements typically contain a higher concentration of EPA and DHA compared to linseed oil. This means you can achieve your desired omega-3 intake with smaller, more manageable doses.
Improved Bioavailability: The molecular modification in ethyl esters enhances their absorption in the body. This ensures that a larger portion of the omega-3 fatty acids reaches the target tissues, maximizing their health benefits.
Reduced Risk of Oxidation: Ethyl esters are less prone to oxidation compared to ALA in linseed oil. Oxidation can compromise the efficacy of the fatty acids and even result in the formation of harmful free radicals.
Greater Omega-3 to Omega-6 Ratio Control: For individuals aiming to balance their omega-3 to omega-6 ratio (favoring omega-3s for their anti-inflammatory properties), ethyl esters provide precise control. This is particularly important in Western diets, which often contain an excess of omega-6 fatty acids.
Clinical Efficacy: Many clinical studies and trials have been conducted using ethyl ester formulations of omega-3s. These studies have demonstrated the efficacy of ethyl esters in supporting cardiovascular health, reducing inflammation, and benefiting brain function.
Reduced Digestive Discomfort: Some individuals may experience digestive discomfort when consuming flaxseed or linseed oil due to their high fiber content. Ethyl ester supplements, on the other hand, are easier on the digestive system.
Conclusion
In the ongoing quest for optimal nutrition and health, choosing the right source of omega-3 fatty acids is crucial. While linseed oil provides alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is beneficial in its own right, ethyl esters offer several advantages, including higher concentrations of EPA and DHA, improved bioavailability, reduced risk of oxidation, and precise control over the omega-3 to omega-6 ratio.
Ultimately, the choice between ethyl esters and linseed oil depends on individual dietary preferences, health goals, and any specific nutritional needs. Consulting with a healthcare provider or nutritionist can help you make an informed decision and incorporate the most suitable omega-3 source into your diet for improved overall well-being.