“Essential” is a term that carries significant weight. It signifies that a particular nutrient is vital for our well-being and must be obtained through our diet since our bodies cannot produce it independently. One such group of essential nutrients is polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). These remarkable molecules play a crucial role in human physiology, impacting various aspects of our health and functioning.
Understanding PUFA
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are a type of fat characterized by their molecular structure, which contains multiple double bonds within their carbon chain. The two primary types of essential PUFA are omega-3 (n-3) and omega-6 (n-6) fatty acids. While both are indispensable, it is their balance in our diet that significantly influences our health.
The Omega-3 Fatty Acids
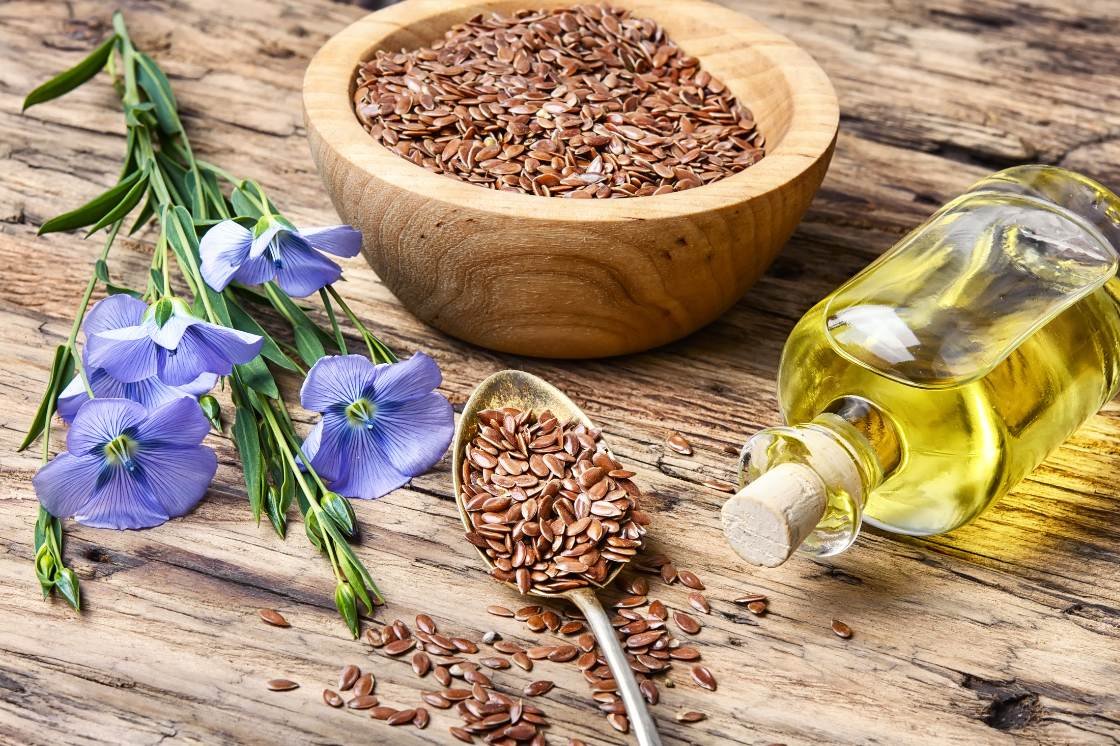
Omega-3 fatty acids, notably eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are renowned for their potent anti-inflammatory properties. These fatty acids are abundant in fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Research suggests that omega-3 fatty acids can:
Support Heart Health: Omega-3s may reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering triglyceride levels, reducing blood pressure, and improving overall cardiovascular function.
Enhance Brain Function: DHA, in particular, is crucial for brain health, aiding in the development of cognitive functions and potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Alleviate Inflammation: These fatty acids can help mitigate chronic inflammation, which is implicated in various diseases, including arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Benefit Mental Health: Omega-3s may have a positive impact on mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety, by supporting neurotransmitter function.
The Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-6 fatty acids, like linoleic acid (LA), are essential for the body’s proper functioning. They are found in vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds. However, the modern Western diet often contains an imbalance of omega-6 to omega-3 ratios, which may contribute to inflammation-related health issues. Maintaining a proper balance is crucial for:
Cell Structure: Omega-6 fatty acids are integral components of cell membranes and play a role in cellular function.
Immune Response: They are involved in the body’s immune response and inflammation regulation.
Hormone Production: Omega-6s are essential for the synthesis of hormones, such as prostaglandins, which regulate various physiological processes.
Balancing Act
The key to reaping the benefits of essential PUFA lies in achieving the right balance between omega-3 and omega-6 intake. Many experts recommend a ratio of roughly 1:1 to 4:1 (omega-6 to omega-3). However, the typical Western diet often features a much higher omega-6 to omega-3 ratio, primarily due to the prevalent use of vegetable oils high in omega-6 fatty acids.
Achieving this balance requires conscious dietary choices. Incorporating fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts into your meals can help boost omega-3 intake. Simultaneously, reducing the consumption of processed foods rich in omega-6 oils can contribute to a healthier ratio.
Conclusion
Essential polyunsaturated fatty acids are aptly named for their indispensable roles in human physiology. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, when consumed in the right balance, can positively influence heart health, brain function, inflammation levels, and overall well-being. By recognizing the importance of these “essential” nutrients and making informed dietary choices, we can promote better health and longevity.